Week 7 - Arrays
Today’s Schedule
- check-in
- midterm review
- help! Classes and Objects
- arrays!
Midterm Exam
We have a take-home midterm exam next week, October 17. It will be uploaded and emailed to you. Your midterm project is due Oct 24. Your exam and midterm project are together worth 15%.
Subjects to review:
- Comments
- Variables
- Types
- randomness
- println debugging
- conditionals
- loops
- functions
- arguments
- return
- translation, rotation, pushMatrix()/popMatrix()
- timer with millis()
- classes and objects
- arrays
Midterm project
Midterm exam will be sent next week. The midterm is to be done solo by you. Do not speak to other students or anyone else besides me about your midterm. I am happy to clarify questions about the midterm but I won’t help you solve any of the problems. You are permitted to use 1. your own notes, 2. your past programs, 3. the processing.org/reference, and 4. the book to complete the midterm, but no other resources, websites, people, etc.
Midterm project is due in two weeks.
Midterm Tamagotchi Project


Part B due next week:
Create your basic program flow in Tab 1 with global variables, setup, draw, and any other needed functions (keypressed, mousepressed, etc). Your draw function should contain a basic way to check what state your creature is in, and to run the relevant code for that state.
Starter example code:
if (state == "sleeping"){
dog.sleeping();
} else if (state == "crying"){
dog.crying();
} else if (state == "eating"){
dog.eating();
} else {
dog.sitting();
}
On tab 2 create your creature’s class in code. You should have a method for each of your creature’s ‘states’.
Part C, the final version, will be to implement timers and interactivity to build the ‘finite state machine’. This part C will be the final version of your project, due in 2 weeks.

Arrays
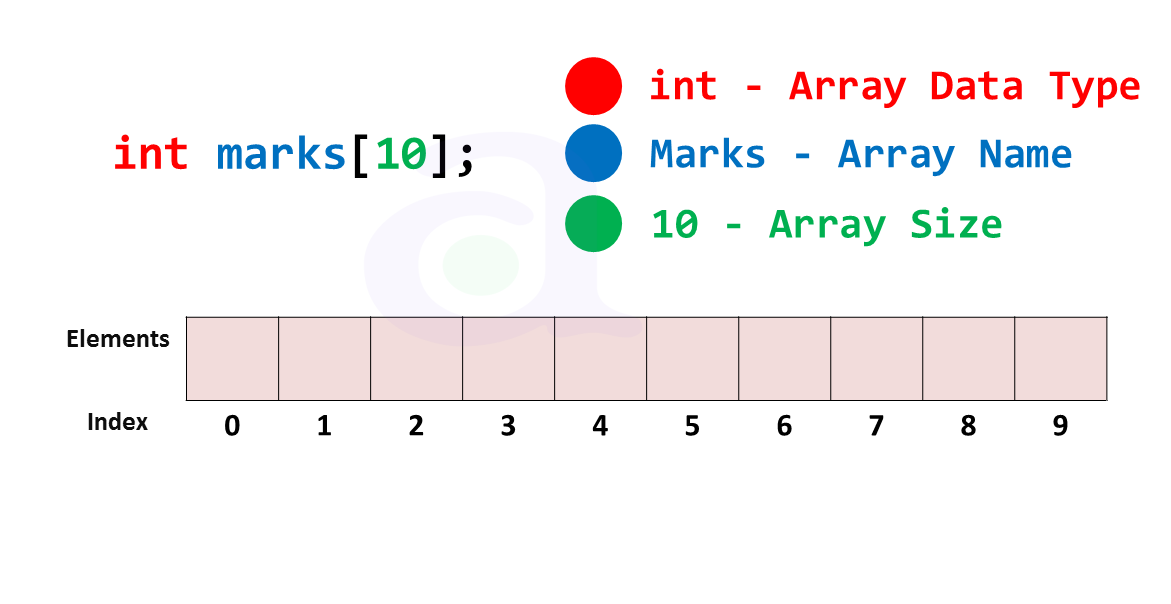
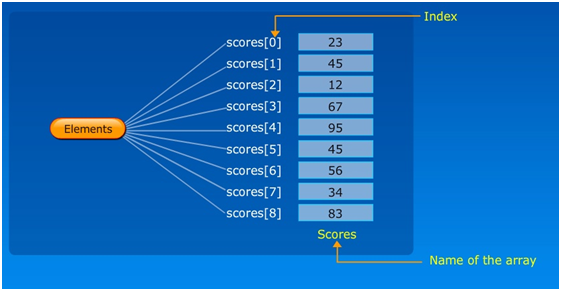
What are they? Arrays are lists. An array is a list of data stored under the same name. You can create an array of any type of data. When you create an array, you can access any of the data stored in that array. We call the location of a piece of data its index.
The first location in an array is always 0. We call that position [0]. The second location is [1]. Etc.
IMPORTANT: Each array has a variable length that returns the total number of elements in the array. Keep in mind that arrays start counting at 0 so an array with 10 elements in (a length of 10) will go from location [0] up to location [9]!
//from Processing tutorials - Arrays
int[] x = {
50, 61, 83, 69, 71, 50, 29, 31, 17, 39
};
fill(0);
// Read one array element each time through the FOR loop
for (int i = 0; i < x.length; i++) {
rect(0, i*10, x[i], 8);
}
Define an Array
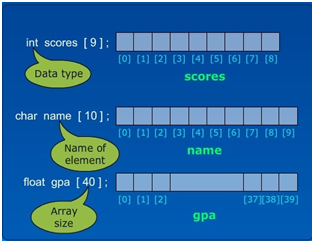
You define an array similar to other data types with the addition of brackets [ and ]. When you declare an array you specify what kind of data it will hold. An array can only hold a single data type.
Three ways to define an array
int[] ages; //declaring an array for BTS members' ages
void setup(){
size(100,100);
ages = new int[7]; //create space in memory for 7 values
ages[0] = 27; //assign
ages[1] = 26;
ages[2] = 25;
ages[3] = 25;
ages[4] = 24;
ages[5] = 24;
ages[6] = 22;
}
OR
int[] ages = new int[7]; //declare and create
void setup(){
size(100,100);
ages[0] = 29; //assign
ages[1] = 29;
ages[2] = 28;
ages[3] = 28;
ages[4] = 26;
ages[5] = 26;
ages[6] = 25;
}
OR
int[] ages_of_BTS_members = {29, 29, 28, 28, 26, 26, 25};
//declare, create and assign all in one
void setup(){
size(100,100);
}
Name array example
String[] names = { "Sleepy","Dopey","Grumpy","Happy","Sneezy","Bashful","Doc" };
void setup(){
size(100,100);
println("Total dwarfs: "+names.length);
println("The first dwarf: "+names[0]);
println("The last dwarf: "+names[names.length-1]);
//question: why do we specify name.length - 1?
}
in-class challenge
How to pick a random dwarf name from the list?
Break it down:
- how many names are there?
- how do you pick a random number between 0 and the total number of names?
- what do you need to do to ‘clean’ up this number (hint: consider that random produces a float)
- how do you print the value stored at that numbered index in the array of names?
Resources
- More about arrays in the Processing reference.
- An additional chapter about arrays from the book Processing: A Programming Handbook for Visual Designers and Artists.
Using loops to initialize an array
Let’s say we wanted to roll 5 dice.
int[] die = new int[5];
die[0] = random(1,7);
die[1] = random(1,7);
die[2] = random(1,7);
die[3] = random(1,7);
die[4] = random(1,7);
die[5] = random(1,7);
Instead, let’s use a loop:
int [] die = new int[5];
for (int i = 0; i < die.length; i++){
die[i] = int(random(1,7));
//must convert from float to int. random produces floats!
}
Remember .length tells us how long the array is
In-class
-
Create an array of 1000 floats. Initialize every element with random number between 0 and 10.
-
Create and initialize an array of 100 integers. Calculate the sum of all elements in the array.
-
Print the lowest value from an array of numbers.
More on arrays
- Arrays are declared similarly to other data types but use a bracket to indicate a list of elements.
- After declaring an array, use
newto create the array.data = new int[5]; - Array’s individual elements may have their value changed, but you cannot change the length of the array.
Where we’re going next: arrays of objects.
Watch
Watch The Coding Train videos on Arrays.