Week 10 - History of Computing and the Layers of Abstraction
Today:
- Autonomous agents (arrays of objects)
- History of computation
History of computation
charles Babbage
- Difference Engine
- analytical engine - 1822
- computation with gears
- The Difference Engine - video
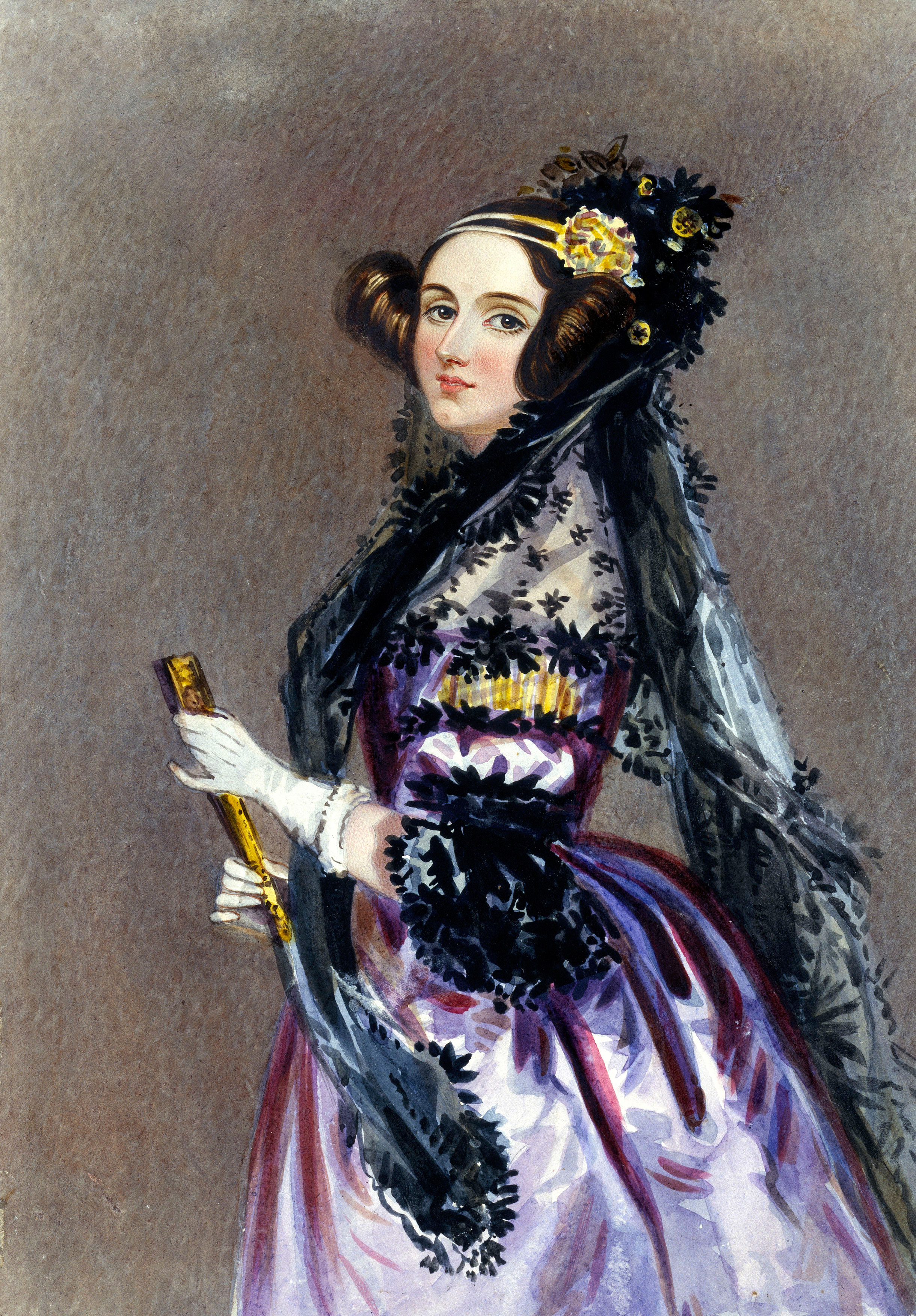
Ada Lovelace
Lady Ada
Augusta Ada King, Countess of Lovelace (née Byron; 10 December 1815 – 27 November 1852) was an English mathematician and writer, chiefly known for her work on Charles Babbage’s proposed mechanical general-purpose computer, the Analytical Engine. She was the first to recognise that the machine had applications beyond pure calculation, and published the first algorithm intended to be carried out by such a machine. As a result, she is sometimes regarded as the first to recognise the full potential of a “computing machine” and the first computer programmer
Lovelace is often considered the first computer programmer, as she was the first to publish an algorithm intended for implementation on Charles Babbage’s analytical engine, in October 1842, intended for the calculation of Bernoulli numbers. Because Babbage’s machine was never completed to a functioning standard in her time, she never saw this algorithm run.

Early Computers
- 1940s computers were very similar to Babbage’s analytical engine but instead of gears they used electronic circuits. To compute (in this case, calculate values), you would physically rewire a circuit.
- over time, banks of switches were introduced to allow you to make changes to a circuit
Von Neumann

- programming was done by throwing switches in a specific way
- in the 1950s John Von Neumann introduced if-then logic, loops and the concept of a subroutine
ENIAC

- Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer) was amongst the earliest electronic general-purpose computers made. It was Turing-complete, digital and able to solve “a large class of numerical problems” through reprogramming.
- Although ENIAC was designed and primarily used to calculate artillery firing tables for the United States Army’s Ballistic Research Laboratory, its first program was a study of the feasibility of the thermonuclear weapon.
- Elizabeth Snyder and Betty Jean Jennings were responsible for developing the demonstration trajectory program, although Herman and Adele Goldstine took credit for it. ENIAC was completed in 1945 and first put to work for practical purposes at the end of that year

Grace Hopper
- She popularized the idea of machine-independent programming languages, which led to the development of COBOL, an early high-level programming language still in use today.
- English words could now be translated into machine code.
- this concept was used by languages Fortran, COBOL and later PASCAL, Algol, BASIC
When Hopper recommended the development of a new programming language that would use entirely English words, she “was told very quickly that [she] couldn’t do this because computers didn’t understand English.” Her idea was not accepted for 3 years, and she published her first paper on the subject, compilers, in 1952. In the early 1950s, the company was taken over by the Remington Rand corporation, and it was while she was working for them that her original compiler work was done. The program was known as the A compiler and its first version was A-0. Wikipedia

Computing
Parts of computing
- you need an editor, compiler and linker
- an IDE (Integrated Development Library) combines all 3
- the end product is that software results in hardware doing something
Writing software - behind the scenes
- write source code
- compile source code into object code
- link the compiled code to libraries needed to build the code
- run it and test it
Abstraction - layers of computing

Binary - Base 2

Adding in Binary - a wooden mechanical ‘computer’ - video
In mathematics and digital electronics, a binary number is a number expressed in the base-2 numeral system or binary numeral system, which uses only two symbols: typically 0 (zero) and 1 (one).
Binary lets us use a system of logic. Truth and False. On and off.
Counting in binary

Optional cute video: Binary for Kids - video
Bits and Bytes
The length of a binary number is the amount of 1’s and 0’s it has. In other words, the number of digits is called the length.
Common bit-lengths of binary numbers include bits, nibbles, and bytes
Each 1 or 0 in a binary number is called a bit.
The byte is a unit of digital information that most commonly consists of eight bits, representing a binary number. Historically, the byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character of text in a computer.
A byte can hold values from 0 to 255.
Homework
Reading assignment
Read Chapter 12, short chapter on Libraries.
Bit Flip assignment
Watch this video from RadioLab about their show on Bit Flip:
Listen to the episode Bit Flip.
Watch this short 8-minute video from Computerphile on Error Detection and Flipping The Bits.
In a paragraph or two, describe what the bit flip problem is.
Answer:
- How did it affect voting?
- What are examples of other things that can be affected by bit flipping?
- What are the implications of this problem? In other words, what can we do to counteract the problem, and/or what actions should we take in society?