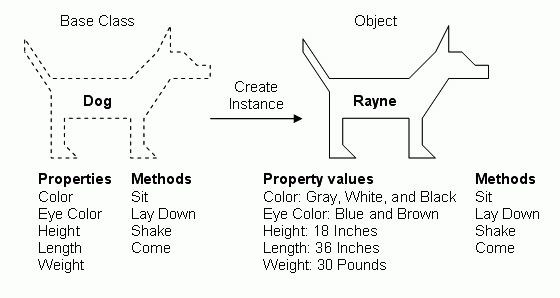
What is a class?
What is an object?
In a programming language, a class is a defined code template that is used to create objects. Objects can have default instance variables and methods (functions). We say that classes encapsulate objects.
- They store functions and variables together
- A class is a template - a cookie-cutter
- They are used to stamp out individual Objects
- When we stamp out or create an object using the Class/cookie cutter we are said to be instantiating an object. Each object is an instance of the class.
Javascript Classes in ES6
ECMAScript6 aka ES6 aka ECMAScript 2015 aka harmony was a large change to Javascript’s implementation across browsers, the first mass-adopted change since 2009. It provides new syntax for classes and objects, modules, variables, loops, functions and more.
There are many ways to create classes and objects in Javascript. Below is a good way to do so using ES6 features.
Writing a class
- At the top of the class is a constructor function
- The constructor is kind of like an object’s setup in that it provides the initial values for any passed variables and it creates new variables that may be used in class
thisis a special keyword in javascript.- Each time you use the class to create a new object instance, it will have its own variables and functions assigned to it
- If I have a class People and a variable name it’s important that my Billy object has the name Billy and if I also make a Sally object it has its name variable be Sally and not Billy. (Sorry for this metaphor)
- We use
thisin front of the variables because each stamped out object will need to reference its own version of that variable - Note that functions inside of classes are called methods. You don’t need to include the word
functionin front of them since they are understood as functions without it. newis the instruction to create an object- it creates an object instance
An Example Class
class Person {
constructor(name,x,y) {
this.name = name; //takes the passed name and sets the local name variable
this.x = x //takes the passed x value
this.y = y //takes the passed y
this.message = "Hi "+this.name;
}
drawName(){
text(this.message,this.x,this.y);
}
function setup(){
wolfgang = new Person("Wolfgang",100,200);
clara = new Person("Clara",200,350);
}
function draw(){
wolfgang.drawName;
clara.drawName;
}
Default arguments
- Default arguments are optional
- You can include default values for the variables connected to each object
- You can specify in the constructor like this:
constructor(x = 100, y = 300)